What is vibration testing, how does it work, and why it is essential
02-06-2023
Understanding Vibration Testing: Assessing Durability and Reliability
Vibration testing is a fundamental method employed to evaluate the endurance and dependability of mechanical and electronic systems. By replicating the stresses and strains encountered in real-world environments, this process plays a pivotal role in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications, where the failure of such systems can have severe consequences.
The Vibration Testing Process in Detail
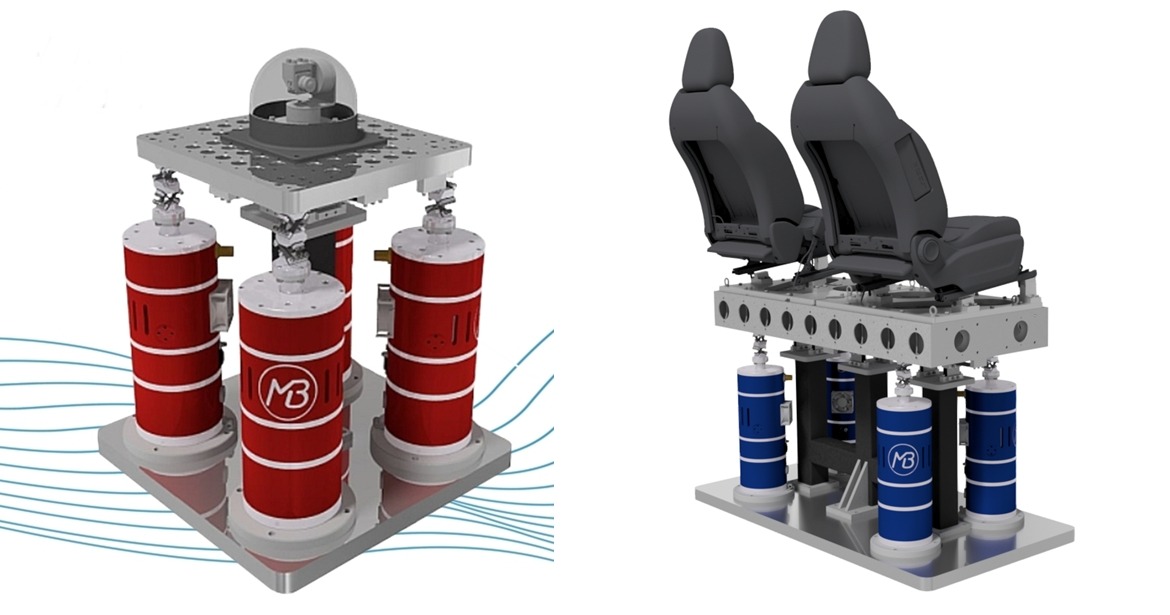
Vibration testing involves subjecting systems or components to a range of frequencies and amplitudes, enabling the measurement of their ability to withstand stress induced by vibrations. The testing apparatus, typically a vibration testing machine, generates vibrations that simulate conditions found during transportation, operation, and other real-world scenarios.
During the testing process, the frequencies most likely to cause failure are identified and applied to the system or component. The vibrations may be applied in a single direction or multiple directions, depending on the specific testing requirements. Adjustments to the amplitude of the vibrations allow for the simulation of various stress levels.
Analyzing the results of vibration testing reveals the performance of the system or component under examination, pinpointing any weaknesses or design flaws that could lead to failure. The data obtained from these tests is then utilized to enhance the design and manufacturing processes, ensuring the reliability and durability of mechanical and electronic systems.
The Significance of Vibration Testing
Vibration testing is of paramount importance due to the potential for mechanical and electronic systems to fail under the stress of vibrations caused by factors like transportation, installation, and normal wear and tear. The consequences of system failure can range from costly recalls and downtime to safety hazards, and in extreme cases, loss of life.
By conducting vibration testing, potential design flaws and manufacturing defects can be identified before systems or components are put into use. This preventive approach mitigates failures, validating the performance and quality of mechanical and electronic systems, and ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Different Types of Vibration Testing
Several types of vibration testing exist, each serving a distinct purpose and requiring specific equipment and procedures. These include:
1. Sine Sweep Testing: This method exposes components to a single sine wave frequency or a gradually changing frequency and amplitude. Sine testing is commonly used to identify resonant frequencies and measure frequency responses.
2. Random Vibration Testing: In this approach, components are subjected to an ever-changing range of frequencies and amplitudes, mimicking real-world environments such as the unpredictable vibrations experienced during road transportation. This method detects weaknesses and defects that may go unnoticed using other testing techniques.
3. Mechanical Shock Testing: This method entails subjecting components to sudden and intense impacts, simulating scenarios like drops and other mechanical shocks. Mechanical shock testing assesses the component's ability to withstand sudden impacts, ensuring its safety in real-world situations.
In conclusion, vibration testing is an indispensable process that guarantees the reliability and durability of mechanical and electronic systems. By subjecting systems and components to various vibration testing methods, manufacturers can identify potential design flaws, manufacturing defects, and weaknesses, thus ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. Vibration testing is a critical factor in upholding the safety and dependability of the products we rely on daily.